- Complex,
- Copper ion,
- Spectrophotometer,
- Oil,
- Neocuproine
Copyright (c) 2019 Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
In the present study, a novel method for determination of copper content in oil samples using Neocuproine reagent was introduced. Copper ion plays a key role in environmental and biological systems which low levels of such material is necessary for living creatures. Copper is poisonous in high concentration, leaving negative effects in natural performance of human bodies. Therefore, the measuring low amount of copper is very important. Spectrophotometry methods to measure copper are based on the absorption of optically active complexes. High detection is considered as a drawback in these methods. Therefore, improving such methods by appropriate and selective complex compounds can lead to complex absorption rise and, in turn, the detection limits improvement. In the proposed method, low amounts of copper(II) ions were converted to copper(I) ions by adding the hydroxylamine hydrochloride as reducing agent. Then, the copper(I) ion was formed a yellow complex by adding 2,9dimethy 1,10 phenanthroline reagent known as Neocuproine. This method shows high sensitivity, good simplicity and accuracy, low cost, and it is applicable for determination of low copper concentration in extracted water samples from oil.
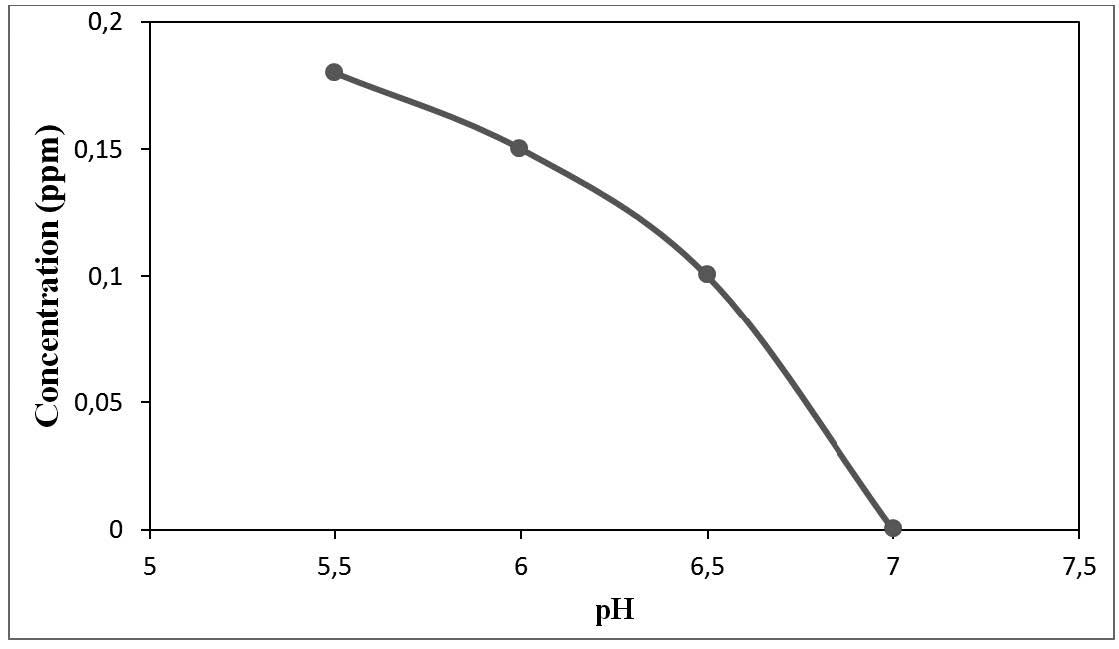
References
- WHO, translated by NouriSepeher – Some Guidelines concerning drinking water, 2nd volume, Hayan Cultural-Publishing institute, Semnan, (1994).
- J.E.Allen, spectrochim. Acta. 17, 467, (1961).
- M.G.Baron, R.T.Herrin, D.E.Armstrong, Analyst, 125, 123-126, (2000).
- M.Dabiri, Environmental pollution (air, soil, water, noise). Tehran: Alliance Publishing 58-160, (1996).
- N.N.Greenwood, A.Earnshaw, Chemistry of the Elements. ElsevierLondon, U.K., (1997).
- M.Resano, M.Aramendía, E.García-Ruiz, C.Crespo, M.A.Belarra, 571, 142- 149, (2006).
- P.Shuklasr, Bioresource Technology 6, 1430-38, (2005).