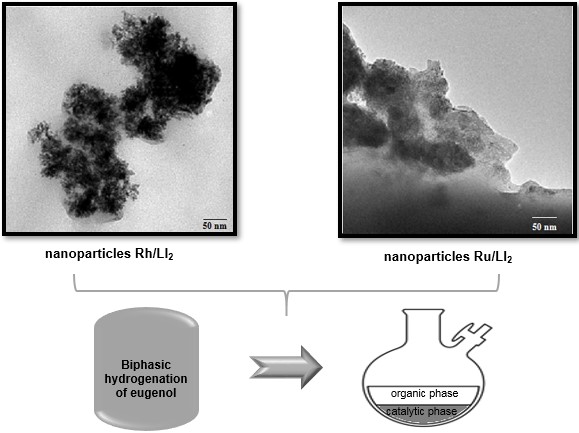
BIPHASIC HYDROGENATION OF EUGENOL WITH RUTHENIUM AND RHODIUM NANOPARTICLES STABILIZED IN IONIC LIQUIDS

- Nanoparticles,
- ionic liquids,
- biphasic hydrogenation,
- eugenol
Copyright (c) 2020 SChQ

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate on the catalytic activity nanostructured systems of ruthenium and rhodium stabilized in ionic liquids derived from imidazole: IL1= butylmethyllimidazole tetrafluoroborate [BMIM][BF4] and IL2= butylmethylimidazole hexafluorophosphate [BMIM][PF6] in the biphasic hydrogenation of eugenol under mild reaction conditions T= 80ºC, P= 100psi during 4 hours. The metallic nanoparticles (NPs-M) were synthesized using the ligand hydrogenation displacement reaction for the ruthenium III tris(acetylacetonate), [Ru(acac)3], and bis-μ-cloro-di(1,5-ciclooctadieno) dirhodium(I), [Rh(COD)Cl]2, showing a mean particle size between (2.00±0.04) nm and (4.0±0.2) nm. The nanostructured systems Rh/IL2, Ru/IL2 and Ru/IL1 show similar activities and different from the Rh/IL1 system. On the other hand, the systems stabilized in the IL1 were more selective towards the formation of the 2-methoxy-4-propylphenol than the systems stabilized in the IL2. Nevertheless, in general, the catalysts were good for hydrogenating eugenol, resulting in Rh/IL1 nanoparticles less reactive than Rh/IL2, Ru/IL1 and Ru/IL2.
References
- P. Baricelli, L. Melean, M. Rodríguez, M. dos Santos, M. Rosales and E. Escalante. Biphasic Hydrogenation and Hydroformylation of Natural Olefins with a Binuclear Rhodium Complex in Ionic Liquid/Toluene. J. Chem. Eng. 7, 299-305, (2013).
- R. González. Eugenol: propiedades farmacológicas y toxicológicas. Ventajas y desventajas de usos. Rev. Cubana Estomatol. V.9,nº2. (2002).
- K. Date, P. Kulkarni. Assessment of Rasadanti in various oral disorders. Ayuved Res. Pap, II, 165-175, (1995).
- Bhimrao. K. Jadhau; Kishanchandra. R. Khandelwal; Avant. R. Ketkar; Sambhaji. S. Pisal. Formulation and evaluation of Mucoadhesive tablets containing eugenol for the treatment of periodontal diseases. Vol 30, Nº 2, pp. 195-203, 2004.
- M. Wie, M. Won, J. Lee; H. Suh; D. Song, Y. Kin. Eugenol protects neuronal cells from excitotoxic and oxidative injury in primary cortical cultives. Neurosci. Lett. 225(2), 93-96, (1997).
- S. Laekeman, V. Hoof, A. Haemers, V. Berghe, A. Harman, A. Vlietink. Eugenol a valuable compound for in-vitro experimental research and worthwhile for further in vivo investigation phytother. Res. 4(3); 99-96. (1990).
- Atsusane, T. Clove oil or dehydroeugenol for controlling oxygen in the human body. Japan. Kokai Tokkyo Koho, 227, 6, (1991).
- Hiroaki, N; Ryui, U; Nozamik, K.S; Kenji, K.J. Role of endotheliom and adventitia on eugenol induced relaxation of rabbit ear artery precontracted by histamine smooth muscle. Res.1998, 34(3), (123-127).
- Demilo AB, Cunningham RT & McGovern TP. Structural of Methyl Eugenol and Their Attractiveness to the Oriental Fruit Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). Journal of Economic Entomology. 87 (4): 957-964, (1994).
- A. Kadarohman. Mempelajari Mekanisme Dan Kontrol Reaksi Isomerisasi Eugenol Menjadi Isoeugenol. Thesis of FMIPA UGM Yogyakarta: Unpublication. (1994).
- A. Kadarohman. Isomerisasi, Hidrogenasi Eugenol, Dan Síntesis Turunan Kariofilena. Dissertation of FMIPA UGM Yogyakarta: Unpublication. (2003).
- Z. Cong, X. Jing, S. Liang, X. Hongchuan, L. Sen, X. Lishu, L. Xuebing. Aqueous-phase hydrodeoxygenation of lignin monomer eugenol:Influence of Si/Al ratio of HZSM-5 on catalytic performances. Catal. Today (2014).
- L. Petitjean , R. Gagne, E. Beach., D. Xiao and P. Anastas. Highly selective hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis using a copper-doped porous metal oxide catalyst. Green Chemistry, 18(1), 150-156, (2016).
- L. Meleán, P. Baricelli, M. Rosales. Hidrogenación e hidroformilación de terpenos, alilbencenos y aldehídos α,β insaturados con complejos hidrosolubles de Rodio y Rutenio en medio bifásico. Tesis Doctoral. UCV, Ven, 8-241, (2010).
- J. Dupont, C. Consorte, P. Suarez, R. De Souza. Preparation of 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium-based room temperature ionic liquids. [1H-Imidazolium, 1-butyl-3-methyl-, chloride (1−); 1H-Imidazolium, 1-butyl-3-methyl-, tetrafluoroborate (1−); 1H-Imidazolium, 1-butyl-3-methyl-, hexafluorophosphate (1−) ]. Org. Syntheses. Coll. 10; 184, (2004).
- J. Dupont, C. Consorti,P. Suarez, R. De Souza. Preparation of 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium-based room temperatura Ionic liquids. Org. Synth, 79, 236. (2002).
- X. Dan-Qian, H. Zhi-Yan, L. Wei-Wei, L. Shu-Ping, X. Zhen-Yuan. Hydrogenation in ionic liquids: An alternative methodology toward highly selective catalysis of halonitrobenzenes to corresponding haloanilines. Journal of molecular catalysis A Chemical 235; 137-142. (2005).
- P. Suarez, J. Dullius; S. Einloft; R. de Souza and J. Dupont; Org. Syntheses. The use of new ionic liquids in two-phase catalytic hidrogenation reaction by Rhodium complexes; Elsivier science, 2 ; 1217-1219, (1996).
- O. Domínguez, E. Escalante, D. Manaure; E. Cañizales, R. Machado. Actividad catalítica de nanopartículas de Rodio estabilizados en diferentes líquidos iónicos en reacciones de hidrogenación del ciclohexeno y del benceno. Revista de la facultad de ingeniería UCV, 27(3), 95-104, (2012).
- Jackson D. Scholten, Martin H.G. Prechtl, and Jairton Dupont. Formation of Nanoparticles Assisted by Ionic Liquids. Handbook of Green Chemistry Volume 8: Green Nanoscience, First Edition (2012).
- M. Sosa, M. Bullón, C. Urbina, G. Jorge, J. Martínez. Estudio de nanopartículas bimetálicas de Rh-Pd sintetizadas por vía electroquímica. Avances en ciencias e ingeniería. Research Gate, Vol 2(3), pp.889-99. (2011).
- M. Ramírez, K. Philippot, B. Chaudret. Influencia del medio de reacción en la estabilización de nanoestructuras de Rodio. Ingeniería investigación y tecnología, 16 (2). 225-237. (2015).
- M. Prechtl, P. Campbell, J. Scholten, G. Frases, G. Machado, C. Santini, J. Dupont, Y. Chauvin. Imidazolium ionic liquids as promoters and stabilising agents for the preparation of metal(0) nanoparticles by reduction and decomposition of organometallic complexes. Nanoscale, 2, 2601-2606, (2010).
- M. Prechtl, M Scariot, J. Sholten, G. Machado, S. Texeira and J. Dupont. Nanoscale Ru(0) particles Arene hydrogenation catalysts in imidazolium ionic liquids inorganic chemistry, vol 47, Nº 19, (2008).
- A. Kadarohman. Kinetics of complex reaction of eugenol hydrogenation to 2-methoxy-4-propylphenol in Pd/Y catalyst. Journal ILMU DASAR.vol11,Nº 1, 1-7. (2010).
- Speziali, M. G; Moura, F.C.C; Robles-Dutenhefner, P.A; Araujo. M.H; Gusevskaya, E.V;Dos Santos. E.N. Selective hydrogenation of myrcene catalyzed by complexes of ruthenium, chromium, iridium and rhodium. J.Mol.Catl.A: Chem, 239,10. (2005).
- Bond, G.C; Louis,C y Thompson, D.T.(2006). Catalysis by Gold. (1a. ed;vol.6).Londres. Imperial. College.Press.
- Corain, B; Schimid, G y Toshima, N. (2008). Metal nanoclusters in catalysis and materials science the issue of control. Ansterdam: Elsevier.
- R. Zanella. Aplicación de los nanomateriales en catálisis. Mundo nano. Vol.7, nº 12, (2014).
- J. Dupont y J. Scholten. On the structural and surface properties of transition-metal nanoparticles in ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev, 39, 1780–1804, (2010).
- S. Kang, K. Char, Y. Kang. Chem Mater 20:1308–1311, (2008).
- J. Dupont, J. Braz. Chem.Soc.15, 341. (2004).
- P. Migowski, G. Machado, S. Texeira., A. Traverse, J. Dupont. Phys.Chem.9 (2007) 4814.
- a) Redel. E, Thomann. R, Janiak. C. Inorg.Chem.47(2008)14; b) Redel. E, Thomann. R, Janiak. C. Chem.Commun (2008) 1789.
- Gutel.T, Garcia-Anton. J, Pelzer.K, Philippot. K, Santimi.C.C, Chauvin.Y, Chaudret.B, Basset. J.M. J.Mater.Chem.17(2007)3290.
- a) Fonseca. G.S, Machado.G, Texeira. S.R, Fecher. G.H, Marais. J, Alves.M.C.M, Dupont.J, J.Colloid interface Sci. 301(2006)193; b) Ren.L, Meng.L, Lu.Q, Fei. Z, Dyson. P.J. J.Colloid interface Sci. 323 (2008) 260.
- Dupont. J. Acc.Chem.Res (2011), 44, 1223-1231.
- Dupont. J, Sholten. J.D. Chem.Soc.Rev. (2010), 39, 1780-1804.
- Wegner,S y Janiak, C. Metal nanoparticles in ionic liquids. Top Curr Chem (Z), 375:65. (2017).
- J. A. Widegren, M. A. Bennett and R. G. Finke, J. Am. Chem. Soc, 125, 10301, (2003).
- A. Reay and I. Fairlamb. Catalytic C–H bond functionalisation chemistry: the case for quasi-heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Commun.1-19, (2005).