- Polyherbal,
- Entocid,
- Catechin,
- HPLC-DAD,
- Digestive syrup
Copyright (c) 2018 Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
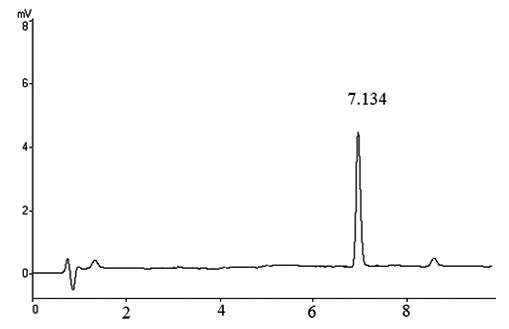
Entocid syrup is a balanced composition of vigilantly selected and formulated with effective herbs of proven efficacy in intestinal ailments covering the segment of hyper-acidity symptoms. Entocid is scientifically formulated in such a way that it not only neutralizes the acid secretion but at the same time it strengthens the stomach thus acts promptly and relieves the symptoms of GI upsets and in the long-run prevents the recurrence of such symptoms. The ingredients of Entocid syrup are rich in alkaloids, proteins, vitamins, glycosides, bioflavonoid and trace elements, formulated using ten potent herbal drugs namely Amomum sabulatum, Berberis aristata, Cinnamomum tamala, Coriandrum sativum, Cuminum cyminum, Foeniculum vulgare, Vitis vinifera, Mesua ferrea, Glycyrrhiza glabra and Mentha piperita. The flavonoid compounds exhibit preventive effects from colon carcinogenesis, lipid lowering effects, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-depressant and anti-atherogenic properties. To develop the assay method, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with a diode-array detector (DAD) was used. Using HPLC/DAD, catechin was eluted with gradient program. The UV characteristic of catechin, the detection wavelength was monitored at 265 nm. Method validation including limit of quantitation, the accuracy, inter and intra day and limitation was performed by using recovery tests. The future development of flavonoids-based drugs is limitation and assumes to provide significant effects on digestion related diseases.
References
- Patra, K. C.; Pareta, S. K.; Harwansh, R. K.; Kumar, K. J., Traditional approaches towards standardization of herbal medicines-A review. J Pharm Sci Technol 2010,2 (11), 372-379.
- Shaikh, S. H.; Malik, F.; James, H.; Abdul, H., Trends in the use of complementary and alternative medicine in Pakistan: a population-based survey. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2009,15 (5), 545-550.
- Hussain, S.; Malik, F.; Riaz, H.; Qayyum, M. A.; Khalid, N., Alternative and Traditional Medicines Systems in Pakistan: History, Regulation, Trends, Usefulness, Challenges, Prospects and Limitations. INTECH Open Access Publisher: 2012.
- Hara, Y., Influence of tea catechins on the digestive tract. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 1997,67 (S27), 52-58.
- Gey, K. F., Ten-year retrospective on the antioxidant hypothesis of arteriosclerosis: Threshold plasma levels of antioxidant micronutrients related to minimum cardiovascular risk. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 1995,6 (4), 206-236.
- (a) Vita, J. A., Tea consumption and cardiovascular disease: effects on endothelial function. The Journal of nutrition 2003,133 (10), 3293S-3297S;(b) Stangl, V.; Lorenz, M.; Stangl, K., The role of tea and tea flavonoids in cardiovascular health. Molecular nutrition & food research 2006,50 (2), 218-228.
- Desai S, Tatke P, Gabhe S, Enhanced HPLC-DAD Method for Fast Determination of Quercetin-3-O-β-D-Glucoside in Extracts and Polyherbal Formulations Containing Azadirachta Indica-Optimization and Validation, J Chromatogr Sci 2017, 1-6.
- Lu Zhao, Wen E, Halmuart Upur, Shuge Tan, High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detector Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Five Compounds in the Pulp and Seed of Sea Buckthorn, Pharmacognosy Magzine, 2017, 13(49), 136-140.
- Alam 1, Ahmed I. Foudah 1, Hala H. Zaatout, Kamal Y T and Maged S. Abdel-Kader. Uantification of glycyrrhizin biomarker in Glycyrrhiza glabra rhizome and baby herbal formulations by validated RP-HPLC methods, Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2017 14(2):198-205.
- Kranti P Musmade, M Trilok, Krishnamurthy Bhat, Virendra S Ligade, Prashant B Musmade & N Udupa, Validation of An Isocratic LC Method For Determination of Quercetin in Developed Nanoformulation, Pharma View , 2014, 103 -113.
- Chobot, V; Huber, C.; Trettenhahn, G.; Hadacek, F.; Catechin: chemical weapon, antioidant, or stress regulator? Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2009, 35 (8),980-996.