ELECTROCATALYTIC OXIDATION AND VOLTAMMETRIC DETERMINATION OF SULFAMETHAZINE USING A MODIFIED CARBON ELECTRODE WITH IONIC LIQUID
- Sulfamethazine,
- carbon paste,
- ionic liquid,
- modified electrodes,
- voltammetry
Copyright (c) 2018 Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
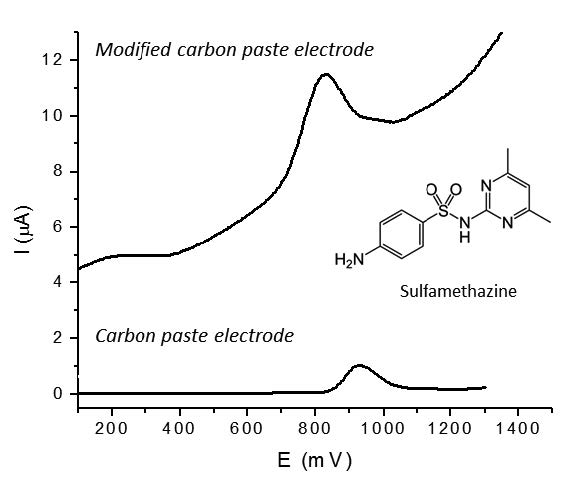
A carbon paste electrode was modified with the ionic liquid 1-methyl-3-octyl imidazolium hexafluorophosphate and it was applied for study the electrocatalytic oxidation and voltammetric determination of the drug sulfamethazine. The developed modified electrode was characterized using cyclic voltammetry and scanning electron microscopy. The oxidation of sulfamethazine at the surface of modified electrode occurs at lower potentials than that of an unmodified carbon paste electrode, and both an enhancement of the anodic peak current and a signal narrower and better defined with the modified electrode were observed. Accordingly, a method for the determination of sulfamethazine was developed using differential pulse voltammetry, at pH 11 and with an accumulation time of 3 min. The oxidation of sulfamethazine exhibited a dynamic range between 30 and 300 μg/mL and detection and quantitation limits of 54 and 61 μg/mL, respectively. The method was applied to the determination of sulfamethazine in a veterinary commercial solution.
References
- C.M. Kahn, S. Line; Merck & Co. The Merck veterinary manual. Whitehouse Station, N.J.: Merck & Co., 2010.
- J.F. Prescott, J.D. Baggott, editors. Antimicrobial therapy in veterinary medicine, 2nd ed. Ames, IA: Iowa State University Press, 1993. p. 119-26.
- J. Appelgate, Mod. Vet. Pract. 667 (1983).
- S.G. Dmitrienko, E.V. Kochuk, V.V. Apyari, V.V. Tolmacheva, Y.A. Zo¬lotov, Anal. Chim. Acta 850, 6 (2014).
- E. Valera, A. Muriano, I. Pividori, F. Sánchez-Baeza, M.P. Marco, Bio¬sens. Bioelectron. 43, 211 (2013).
- G.-F. Pang, Y.-Z. Cao, C.-L. Fan, J.-J. Zhang, X.-M. Li, Z.-Y. Li, G.-Q. Jia, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 376, 534 (2003).
- S. Su, M. Zhang, B. Li, H. Zhang, X. Dong, Talanta 76, 1141 (2008).
- C.-K. Tsai, C.-S. Lin, W.-H. Wang, J. Food Drug Anal. 20, 674 (2012).
- S. Ansari, M. Karimi, Talanta 164, 612 (2017).
- H. Sangjarusvichai, W. Dungchai, W. Siangproh, O. Chailapakul, Talanta 79, 1036 (2009).
- T.N. Rao, B.V. Sarada, D.A. Tryk, A. Fujishima, J. Electroanal. Chem. 491, 175 (2000).
- I. Saidi, I. Soutrel, F. Fourcade, A. Amrane, D. Floner, N. Bellakhal, F. Geneste, J. Electroanal. Chem. 707, 122 (2013).
- I. Cesarino, R. Plana Simões, F.C. Lavarda, A. Batagin-Neto, Electrochim. Acta 192, 8 (2016).
- T.A.M. Msagati, J.C. Ngila, Talanta 58, 605 (2002).
- A. Guzman-Vazquez de Prada, A.J. Reviejo, J.M. Pingarrón, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 40, 281 (2006).
- Y.L. Su, S.H. Cheng, Talanta 180, 81 (2018).
- A. Afkhami, H. Bagheri, A. Shirzadmehr, H. Khoshsafar, P. Hashemi, Electroanalysis 24, 2176 (2012).
- X. Yu, Y. Chen, L. Chang, L. Zhou, F. Tang, X. Wu, Sens. Actuators B 186, 648 (2013).
- W. Sun, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Ju, G. Li, Z. Sun, Anal. Chim. Acta 751, 59 (2012).
- B.N. Chandrashekar, B.E. Kumara Swamy, N.B. Ashoka, M. Pandurangachar, J. Mol. Liq. 165, 168 (2012).
- F. Anson, Anal. Chem. 36, 932 (1964).
- R. Adams, Electrochemistry at Solid Electrodes, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1969.
- Ş. Nurullah, Ş. Senem, Ö. Güleren, A. Denizlic, J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 21,1952 (2010).
- J. Riviere, A.L. Craigmill, S.F. Sundlof, Handbook of comparative phar¬macokinetics and residues of veterinary antimicrobials. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, Inc., 1991. p. 339-407.
- O.A. Quattrochi, S. A. De Andrizzi, R. F. Laba, Introducción a la HPLC, Aplicación y Práctica, Artes Gráficas Farro, SA, Argentina 1992.
- B. Cancho Grande, M.S. García Falcón, M. Rodríguez Comesaña, J. Simal Gándara, J. Agric. Food Chem. 49,3145 (2001).