EFFECT OF CATIONIC MICELLES OF CETYLTRIMETHYLAMMONIUM BROMIDE ON PROTONATION EQUILIBRIA OF SALICYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
- Protonation equilibria,
- MINIQUAD75,
- Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide,
- 5-Sulphosalicylic acid and 5-Hydroxysalicylic acid
Copyright (c) 2018 Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
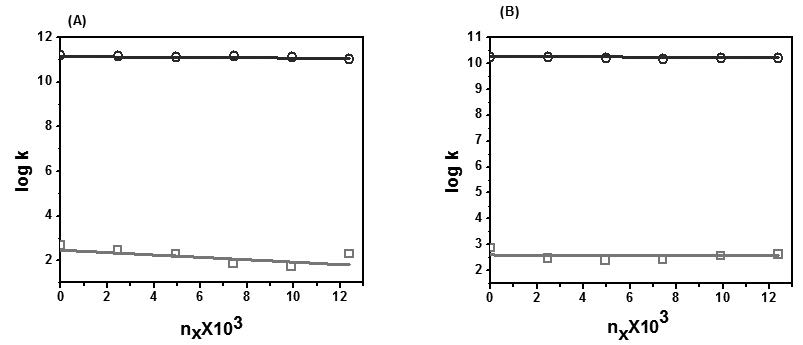
To gain more information about the effect of surfactant on salicylic acid derivatives, the stoichiometric protonation constants of 5-Sulphosalicylic acid and 5-Hydroxysalicylic acid in 0.0%-2.5% (w/v) cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) - water mixtures were determined at an ionic strength of 0.16 mol dm-3 and at 303 K. A potentiometric method was used and the calculation of constants was carried out using the computer program MINIQUAD75. These protonation constants values have been found to shift in micellar media as compared to those in pure water. The differences in the values have been attributed to the solvent properties of the interfacial and bulk phases involving contribution from the micellar surface potential in the case of charged micelles. The trend of log values of step-wise protonation constants with mole fraction of the medium have been explained based on specific solute-solvent interactions. In this study Distributions of species, percentage of species composition, protonation equilibria and effect of influential parameters on the protonation were also discussed.
References
- E. Pelizetti, E. Pramaro, Anal. Chim. Acta. 169, 1, (1983).
- P. Ezzio, P. Edmondo, Anal. Chim. Acta. 117, 403, (1980).
- C. J. Drummond, F. Grieser, T. W. Healy, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans.1. 85, 521, (1989).
- G. S. Hartley, Trans Faraday Soc. 30, 444, (1934).
- G. S. Hartley, J. W. Roe, Trans. Faraday Soc. 36, 101, (1940).
- C. A. Bunton, Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 20, 1, (1979).
- C. A. Bunton, L. S. Romsted, L. Sepulveda, J. Phys. Chem. 84, 2611, (1980).
- H. Chaimovich, M. J. Politi, J. B. S. Bonilha, F. H. Quina, J. Phys. Chem. 83, 1951, (1979).
- R. S. Rao, G. N. Rao, Computer Applications in Chemistry, Himalaya Publishing House, Mumbai, 2005, 302-309.
- G. Gran, Analyst. 77, 661, (1952).
- G. Gran, Anal. Chim. Acta. 206, 111 (1988).
- M. Ramanaiah, B. B.V. Sailaja, Chem. Speciat. Bioavail. 26, 119, (2014).
- M. Ramanaiah, S. Goutham sri, B. B.V. Sailaja, Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop, 28, 383, (2014).
- K. V. S. Devi, B. Ramaraju, G. N Rao, Acta. Chimica. Slovenica. 57, 398, (2010).
- B. Ramaraju, K. V. S. Devi, N. Padmaja, G. N. Rao, J. Indian Chem. Soc. 56, 842, (2011).
- M. Ramanaiah, P Seetharam, B. B.V. Sailaja, J. Indian Chem. Soc. 91, 1011, (2014).
- P. Gans, A. Sabatini and A. Vacca, Inorg. Chim. Acta. 18, 237, (1976).
- M. Ramanaiah, CH. Nageswara Rao, B. B.V. Sailaja, Proc. National Acad. Sci. India. 84, 485, (2014).
- H. Schneider, Top. Curr. Chem. 68, 103, (1976).
- D. Feakins, R. D. O. Neille, W. E. Woghonie, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1. 79, 2289, (1983).
- M. Born, Z. Phys. 1, 45, (1920).