- Partial oxidation,
- butane,
- Co/γ-Al2O3,
- particle size,
- selectivity
Copyright (c) 2017 Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
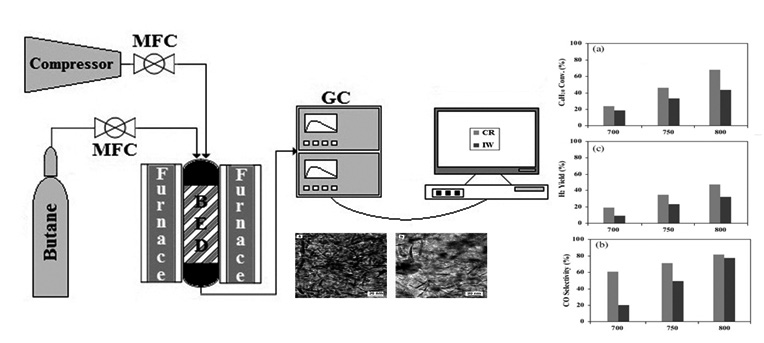
In this study, performance of nano structure Co/γ-Al2O3 catalysts in partial oxidation of butane was investigated. The catalysts were produced through chemical reduction and incipient wetness impregnation methods. Prepared catalysts were characterized with X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), N2 adsorption/desorption (BET), temperature programmed reduction (TPR) and thermal gravity analysis (TGA).The characterization results confirmed the uniform dispersion of Co nanoparticles over γ-Al2O3 by using chemical reduction. Butane conversion, H2 and CO selectivities increased by decreasing of Co particle size due to higher dispersion and reducibility. The optimum value of H2/CO ratio of 2 obtained from chemical reduction technique. The results showed that the stability of catalyst produced by chemical reduction method was higher than incipient wetness impregnation ones.
References
- A.Mosayebi,R.Abedini, Partial oxidation of butane to syngas using nanostructureNi/zeolite catalysts, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 1542,1548, (2014).
- A.S. Larimi, S.M.Alavi, Ceria-Zirconia supported Ni catalysts for partial oxidation of methane to synthesis gas, Fuel. 102, 366,371, (2012).
- E. Iglesia, S.L. Soled, R.A. Fiato, Dispersion, support, and bimetallic effects in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on cobalt catalysts, Stu. Sur. Sci. catal. 81,433,442(1994).
- J.Y. Park, Y.J.Lee, P.R.karandikar, Fischer-Tropsch catalysyts deposited with size controlled Co3O4 nanocrystals: effect of partivle size on catalytic activity and stability, Appl. Catal. A. Gen. 411 ,23,28, (2012).
- S.Sun, N.Tesubaki, K. Fugimito, Novel utilization of mesoporous molecular sieves as supports of cobalt catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, Appl.Catal.A.Gen. 202, 121,131, (2000).
- G.Leendert Bezemer, J.H.Bitter, H.P.Kuipers, H.Oosterbeek, J.E.Holewijin, Cobalt Particle Size Effects in the Fischer-Tropsch Reaction Studied with Carbon Nanofiber Supported Catalysts, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 3956,3963, (2006).
- A. Haghtalab, A. Mosayebi, Co@Ru nanoparticle with core-shell structure supported over Al2O3 for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 39 ,18882,18893, (2014).
- Y.P. Li, T.J. Wang, C.Z. Wua, X.X. Qin, N. Tsubaki, Effect of Ru addition to catalysts on Fischer–Tropsch synthesis of gasoline-range hydrocarbons, Catal.Commun. 10 , 1868,1874, (2009).
- A. Mosayebi, A. Haghtalab, The comprehensive kinetic modeling of the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over Co@Ru/c-Al2O3 core-shell structure catalyst, Chem. Eng. J. 259, 191,204, (2015).
- A.Mosayebi,M.A. Mehrpouya, R. Abedini,The development of new comprehensive kinetic modeling for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis process over Co-Ru/Al2O3 nano-catalyst in a fixed-bed reactor, Chem.Eng.J. 286 ,416,426, (2016).
- M.Trepanier, A.K.Dalai, N.Abtazaglou, Synthesis of CNT-supported cobalt nanoparticle catalysts using a microemulsion technique: Role of particle size on reducibility, activity and selectivity in Fischer–Tropsch reactions, Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 374, 79,86, (2010).
- R. Sabori, S. Sharifnia, M.E. Alami, M.R. Panahi,Promotion of Metallic Catalysts by Metal Oxide Powders in Partial Oxidation of Methane, J. Taiwan. Ins. Chem. Eng. 43, 153,158, (2012).
- A.C.Ferreira,A.M.Ferraria, A.M.Botelho, A.P.Gonc¸ M.Correia,Partial oxidation of methane over bimetallic nickel–lanthanide oxides. J. Alloys. Compd. 489 ,316,322, (2010).
- Y.Wei, H.Wang, K. Li, Ce–Fe–O mixed oxide as oxygen carrier for the directpartial oxidation of methane to syngas. J. Rare. Earths. 28 ,560,567, (2010).
- J.Zhang, N.Zhao, W.Wei, Y.Sun, Partial oxidation of methane over Ni/ Mg/Al/Lamixed oxides prepared from layered double hydrotalcites, Int. J. Hydrogen.Energ. 35,11776,1174, (2010).
- S. Liu, L. Xu, S.J. Xie, Q.X. Wang, Partial oxidation of butane to syngas over nickel supported catalysts modified by alkali metal oxide and rare-earth metal oxide, Chin. Chem. Lett. 12,43, (2001).
- J. Rickenbach, M. Nabavi, I. Zinovik, N.N. Hotz, D. Poulikakos, A detailed surface reaction model for syngas production from butane over Rhodium catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 36 ,12238, (2011).
- N. Hotz, M.J. Stutz, S. Loher, W.J. Stark, D. Poulikakos, Syngas production from butane using a flame-made Rh/Ce0.5Zr0.5o2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B. 73,336. (2007).