ONE-POT GREEN SYNTHESIS OF FLUORESCENT-QUANTUM CARBON DOTS FROM AVOCADO PEELS AND EVALUATION OF ITS ANTIMICROBIAL PROPETIES

- Quantum carbon dots,
- Hydrothermal,
- Avocado peels,
- HPLC
Copyright (c) 2025 JCChemS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
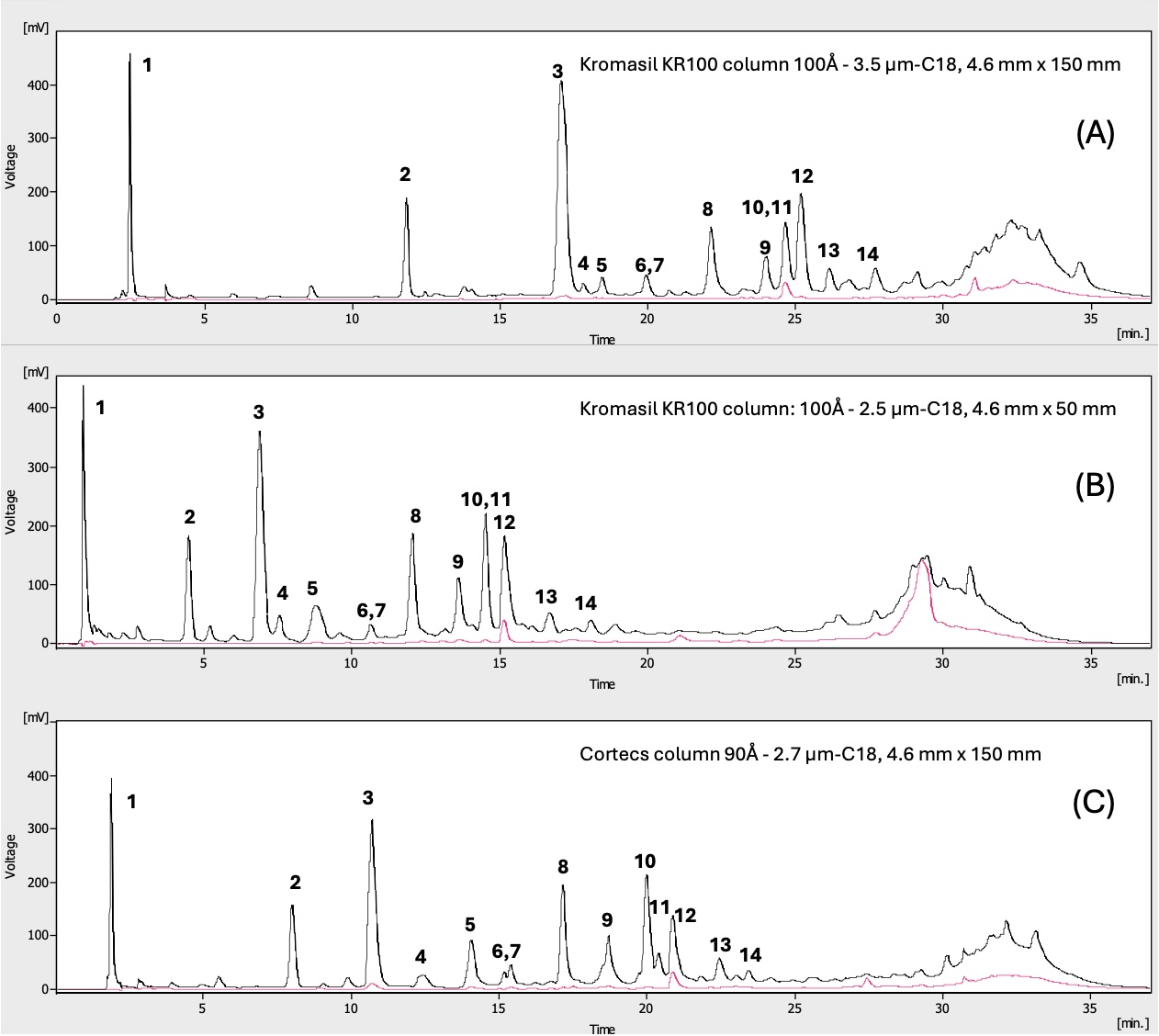
In this work, avocado peel was chosen as a low-value waste that could be used as a carbon source to synthesize carbon dots (APCQDs). To obtain it, the hydrothermal method was used in the absence of co-doping agents. The synthesis was carried out for 6 hours at 250 ºC. After purification by dialysis and lyophilization, CQDs that exhibited intense blue fluorescence (emission at 378 nm) were obtained. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), evidence the spherical morphology of carbon dots within nanometer range. HPLC analysis and separation showed excellent separation even in columns with low porosity, indicating a separation mechanism where polarity predominates as the property that governs the separation. It is highlighted that avocado peel CQDs have potent antimicrobial activity against the pathogens Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 7644, Escherichia coli ATCC 11775, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 9144, and Salmonella enterica ATCC 13076. The antioxidant effect was also evidenced in the DPPH and ORAC-FL. The synthesis method for APCQDs could be easily scaled up for gram scale synthesis of carbon quantum dots.
References
- Meng, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Lu, S.; Yang, B. Biomass‐Derived Carbon Dots and Their Applications. ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL MATERIALS 2019, 2, 172–192, doi:10.1002/eem2.12038.
- Banger, A.; Gautam, S.; Jadoun, S.; Jangid, N.K.; Srivastava, A.; Pulidindi, I.N.; Dwivedi, J.; Srivastava, M. Synthetic Methods and Applications of Carbon Nanodots. Catalysts 2023, 13, 858, doi:10.3390/catal13050858.
- Prasannan, A.; Imae, T. One-Pot Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Orange Waste Peels. Ind Eng Chem Res 2013, 52, 15673–15678, doi:10.1021/ie402421s.
- de Oliveira, B.P.; da Silva Abreu, F.O.M. Carbon Quantum Dots Synthesis from Waste and By-Products: Perspectives and Challenges. Mater Lett 2021, 282, 128764, doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128764.
- Khairol Anuar, N.K.; Tan, H.L.; Lim, Y.P.; So’aib, M.S.; Abu Bakar, N.F. A Review on Multifunctional Carbon-Dots Synthesized From Biomass Waste: Design/ Fabrication, Characterization and Applications. Front Energy Res 2021, 9, doi:10.3389/fenrg.2021.626549.
- Cailotto, S.; Massari, D.; Gigli, M.; Campalani, C.; Bonini, M.; You, S.; Vomiero, A.; Selva, M.; Perosa, A.; Crestini, C. N-Doped Carbon Dot Hydrogels from Brewing Waste for Photocatalytic Wastewater Treatment. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 4052–4061, doi:10.1021/acsomega.1c05403.
- Sharma, A.; Das, J. Small Molecules Derived Carbon Dots: Synthesis and Applications in Sensing, Catalysis, Imaging, and Biomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology 2019, 17, 92, doi:10.1186/s12951-019-0525-8.
- Gedda, G.; Bhupathi, A.; Balaji Gupta Tiruveedhi, V.L.N. Naturally Derived Carbon Dots as Bioimaging Agents. In Biomechanics and Functional Tissue Engineering; IntechOpen, 2021.
- Han, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Ye, J. Preparation of Carbon Quantum Dot Fluorescent Probe from Waste Fruit Peel and Its Use for the Detection of Dopamine. RSC Adv 2024, 14, 1813–1821, doi:10.1039/D3RA06799H.
- Khairol Anuar, N.K.; Tan, H.L.; Lim, Y.P.; So’aib, M.S.; Abu Bakar, N.F. A Review on Multifunctional Carbon-Dots Synthesized From Biomass Waste: Design/ Fabrication, Characterization and Applications. Front Energy Res 2021, 9, doi:10.3389/fenrg.2021.626549.
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications. ACS Cent Sci 2020, 6, 2179–2195, doi:10.1021/acscentsci.0c01306.
- Figueroa, J.G.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Del Pino-García, R.; Curiel, J.A.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Segura-Carretero, A. Functional Ingredient from Avocado Peel: Microwave-Assisted Extraction, Characterization and Potential Applications for the Food Industry. Food Chem 2021, 352, 129300, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129300.
- Saavedra, J.; Córdova, A.; Navarro, R.; Díaz-Calderón, P.; Fuentealba, C.; Astudillo-Castro, C.; Toledo, L.; Enrione, J.; Galvez, L. Industrial Avocado Waste: Functional Compounds Preservation by Convective Drying Process. J Food Eng 2017, 198, 81–90, doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.11.018.
- Araújo, R.G.; Rodriguez-Jasso, R.M.; Ruiz, H.A.; Pintado, M.M.E.; Aguilar, C.N. Avocado By-Products: Nutritional and Functional Properties. Trends Food Sci Technol 2018, 80, 51–60, doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2018.07.027.
- Calderón-Oliver, M.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B.; Medina-Campos, O.N.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Pedroza-Islas, R.; Ponce-Alquicira, E. Optimization of the Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Response of the Combined Effect of Nisin and Avocado Byproducts. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2016, 65, 46–52, doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2015.07.048.
- Segovia, F.J.; Corral-Pérez, J.J.; Almajano, M.P. Avocado Seed: Modeling Extraction of Bioactive Compounds. Ind Crops Prod 2016, 85, 213–220, doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.03.005.
- Chávez, F.; Aranda, M.; García, A.; Pastene, E. Antioxidant Polyphenols Extracted from Avocado Epicarp (Persea Americana Var. Hass) Inhibit Helicobacter Pylori Urease. Bol Latinoam Caribe Plantas Med Aromat 2011, 10.
- Cui, L.; Ren, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Xia, L. Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3419, doi:10.3390/nano11123419.
- Kuang, T.; Jin, M.; Lu, X.; Liu, T.; Vahabi, H.; Gu, Z.; Gong, X. Functional Carbon Dots Derived from Biomass and Plastic Wastes. Green Chemistry 2023, 25, 6581–6602, doi:10.1039/D3GC01763J.
- Mishra, K.; Ojha, H.; Chaudhury, N.K. Estimation of Antiradical Properties of Antioxidants Using DPPH Assay: A Critical Review and Results. Food Chem 2012, 130, 1036–1043, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.127.
- Kassim, N.K.; Rahmani, M.; Ismail, A.; Sukari, M.A.; Ee, G.C.L.; Nasir, N.M.; Awang, K. Antioxidant Activity-Guided Separation of Coumarins and Lignan from Melicope Glabra (Rutaceae). Food Chem 2013, 139, 87–92, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.01.108.
- Adhikari, B.; Shah, P.K.; Karki, R. Antibiogram and Phytochemical Analysis of Cinnamon, Clove, and Sichuan Pepper Extracts. Nepal Journal of Biotechnology 2021, 9, 1–7, doi:10.3126/njb.v9i1.38644.
- Kumar, M.S.; Yasoda, K.Y.; Kumaresan, D.; Kothurkar, N.K.; Batabyal, S.K. TiO 2 -Carbon Quantum Dots (CQD) Nanohybrid: Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. Mater Res Express 2018, 5, 075502, doi:10.1088/2053-1591/aacbb9.
- Wang, B.; Lu, S. The Light of Carbon Dots: From Mechanism to Applications. Matter 2022, 5, 110–149, doi:10.1016/j.matt.2021.10.016.
- Rooj, B.; Mandal, U. A Review on Characterization of Carbon Quantum Dots. Vietnam Journal of Chemistry 2023, 61, 693–718, doi:10.1002/vjch.202300022.
- Ren, J.; Stagi, L.; Innocenzi, P. Fluorescent Carbon Dots in Solid-State: From Nanostructures to Functional Devices. Progress in Solid State Chemistry 2021, 62, 100295, doi:10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2020.100295.
- Shaikh, A.F.; Tamboli, M.S.; Patil, R.H.; Bhan, A.; Ambekar, J.D.; Kale, B.B. Bioinspired Carbon Quantum Dots: An Antibiofilm Agents. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2019, 19, 2339–2345, doi:10.1166/jnn.2019.16537.
- Döring, A.; Ushakova, E.; Rogach, A.L. Chiral Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Emerging Applications. Light Sci Appl 2022, 11, 75, doi:10.1038/s41377-022-00764-1.
- Kumari, M.; Chaudhary, G.R.; Chaudhary, S.; Huang, M.; Guo, Z. Transformation of Waste Rice Straw to Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Potential Chemical Sensing Application: Green and Sustainable Approach to Overcome Stubble Burning Issues. Biomass Convers Biorefin 2022, doi:10.1007/s13399-022-02761-1.
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491, doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b05406.
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. Separation of Carbon Quantum Dots on a C18 Column by Binary Gradient Elution via HPLC. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8124–8128, doi:10.1039/C4AY01052C.
- Hayes, R.; Ahmed, A.; Edge, T.; Zhang, H. Core–Shell Particles: Preparation, Fundamentals and Applications in High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J Chromatogr A 2014, 1357, 36–52, doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.05.010.
- Oláh, E.; Fekete, S.; Fekete, J.; Ganzler, K. Comparative Study of New Shell-Type, Sub-2μm Fully Porous and Monolith Stationary Phases, Focusing on Mass-Transfer Resistance. J Chromatogr A 2010, 1217, 3642–3653, doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.03.052.
- Pirok, B.W.J.; Breuer, P.; Hoppe, S.J.M.; Chitty, M.; Welch, E.; Farkas, T.; van der Wal, S.; Peters, R.; Schoenmakers, P.J. Size-Exclusion Chromatography Using Core-Shell Particles. J Chromatogr A 2017, 1486, 96–102, doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.015.
- Chen, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Chang, C.-W. Evaluation of the Dialysis Time Required for Carbon Dots by HPLC and the Properties of Carbon Dots after HPLC Fractionation. New Journal of Chemistry 2019, 43, 6153–6159, doi:10.1039/C9NJ00434C.
- Gong, X.; Hu, Q.; Paau, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Choi, M.M.F. Red-Green-Blue Fluorescent Hollow Carbon Nanoparticles Isolated from Chromatographic Fractions for Cellular Imaging. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8162, doi:10.1039/c4nr01453g.
- Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Carbon Dots for Killing Microorganisms: An Update since 2019. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1236, doi:10.3390/ph15101236.
- Ghirardello, M.; Ramos-Soriano, J.; Galan, M.C. Carbon Dots as an Emergent Class of Antimicrobial Agents. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1877, doi:10.3390/nano11081877.
- Norouzi, N.; Nusantara, A.C.; Ong, Y.; Hamoh, T.; Nie, L.; Morita, A.; Zhang, Y.; Mzyk, A.; Schirhagl, R. Relaxometry for Detecting Free Radical Generation during Bacteria’s Response to Antibiotics. Carbon N Y 2022, 199, 444–452, doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2022.08.025.
- Dong, X.; Liang, W.; Meziani, M.J.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Carbon Dots as Potent Antimicrobial Agents. Theranostics 2020, 10, 671–686, doi:10.7150/thno.39863.
- Das, S.; Ngashangva, L.; Mog, H.; Gogoi, S.; Goswami, P. An Insight into the Mechanism of Peroxidase-like Activity of Carbon Dots. Opt Mater (Amst) 2021, 115, 111017, doi:10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111017.
- Bandi, R.; Alle, M.; Dadigala, R.; Park, C.-W.; Han, S.-Y.; Kwon, G.-J.; Kim, J.-C.; Lee, S.-H. Integrating the High Peroxidase Activity of Carbon Dots with Easy Recyclability: Immobilization on Dialdehyde Cellulose Nanofibrils and Cholesterol Detection. Appl Mater Today 2022, 26, 101286, doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2021.101286.
- Yuan, C.; Qin, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, Y. Carbon Quantum Dots Originated from Chicken Blood as Peroxidase Mimics for Colorimetric Detection of Biothiols. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 2020, 396, 112529, doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112529.
- Jacinth Gracia, K.D.; Thavamani, S.S.; Amaladhas, T.P.; Devanesan, S.; Ahmed, M.; Kannan, M.M. Valorisation of Bio-Derived Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Metal Sensing, DNA Binding and Bioimaging. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134128, doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134128.
- Travlou, N.A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Algarra, M.; Labella, A.M.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Bandosz, T.J. S- and N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots: Surface Chemistry Dependent Antibacterial Activity. Carbon N Y 2018, 135, 104–111, doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2018.04.018.
- Daphne Jacinth Gracia, K.; Muthukumar Sivaraman, R.; Sheeba Thavamani, S.; Peter Amaladhas, T.; Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Balakrishnan, M. Nitrogen Doped Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Delonix Regia for Fe(III) and Cysteine Sensing, DNA Binding and Bioimaging. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2023, 16, 105109, doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.105109.
- Li, F.; Cai, Q.; Hao, X.; Zhao, C.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, X.; Weng, S. Insight into the DNA Adsorption on Nitrogen-Doped Positive Carbon Dots. RSC Adv 2019, 9, 12462–12469, doi:10.1039/C9RA00881K.
- Christensen, I.L.; Sun, Y.-P.; Juzenas, P. Carbon Dots as Antioxidants and Prooxidants. J Biomed Nanotechnol 2011, 7, 667–676, doi:10.1166/jbn.2011.1334.
- Innocenzi, P.; Stagi, L. Carbon Dots as Oxidant-Antioxidant Nanomaterials, Understanding the Structure-Properties Relationship. A Critical Review. Nano Today 2023, 50, 101837, doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2023.101837.
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, S.; Huang, C.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y.; Song, R.-B.; Li, Z. Carbon Dots as Light-Responsive Oxidase-like Nanozyme for Colorimetric Detection of Total Antioxidant Capacity in Fruits. Food Chem 2023, 405, 134749, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134749.
- Gao, F.; Liu, J.; Gong, P.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Carbon Dots as Potential Antioxidants for the Scavenging of Multi-Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 462, 142338, doi:10.1016/j.cej.2023.142338.
- Ortiz, R.; Antilén, M.; Speisky, H.; Aliaga, M.E.; López-Alarcón, C.; Baugh, S. Application of a Microplate-Based ORAC-Pyrogallol Red Assay for the Estimation of Antioxidant Capacity: First Action 2012.03. J AOAC Int 2012, 95, 1558–1561, doi:10.5740/jaoacint.CS2012_03.