- Chitosan,
- Carbon nanotubes,
- Quantum dots,
- Fish toxicity
Copyright (c) 2022 SChQ

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
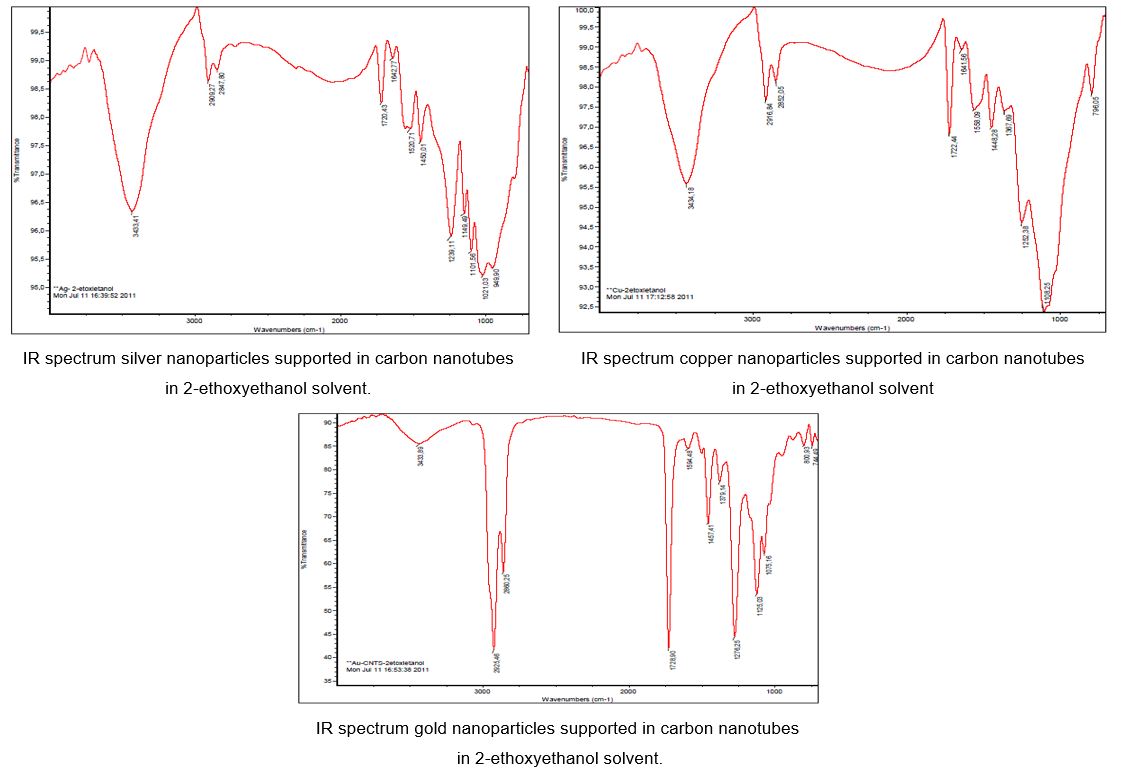
The synthesis of Au, Ag and Cu metal nanoparticles in 2-ethoxyethanol and 2-propanol supported in carbon nanotubes is reported. The synthesis was carried out by chemical liquid deposition (CLD) at 77K to obtain metal colloids. The metal supported in carbon nanotubes was obtained by solvated metal atom dispersed (SMAD) method. The composites were characterized by electron microscopy with electron diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, elemental analysis, thermogravimetry, infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The quantum dots size in 2-propanol and carbon nanotubes supported are: silver 4.37 nm and copper 2.56 nm. In 2-ethoxyethanol solvent: silver 4.14 nm, copper 2.47 nm and gold 5.30 nm. The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images confirm the presence of quantum dots inside and outside the carbon nanotubes. The samples demonstrate a thermal stability until 295°C. The FTIR exhibit the presence of solvent residues in the samples. The electron diffraction is observed in the silver and copper in 2-propanol supported in carbon nanotubes and in the silver sample for 2-ethoxyethanol. The histological analyses of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after being injected with gold quantum dots in 2-ethoxyethanol, in concentrations 0.5 and 0.3x10-3 M do not exhibit cell disruption showing hepatocytes with morphology according to the normal for that specie.
References
[2] CH. Pooler and F. Owens. Introducción a la Nanotecnología. Primera Edición. (Editorial Reverté, 2007) pp. 81.
[3] ETC Group 2006. www.etcgroup.org.es
[4] Banerjee, D., Harfouche, R. & Sengupta, S. Nanotechnology-mediated targeting of tumor angiogenesis. Vasc Cell 3, 3 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-824X-3-3.
[5] Ministerio de Salud, Guía Clínica AUGE “Artritis Reumatoidea”, MINSAL 2013.
[6] M. Matteini and A. Moles. La Química en la restauración: los metales del arte pictórico. 1ª Edición. (Editorial Nerea, 2001) pp. 89
[7]M.F. Hornos Carneiro, F. Barbosa Jr. J. Toxicol. Environ Health B Crit Rev 2016 (3-4)129-48. Doi: 10.1080/10937404.2016
[8] A. Laguna, M. Concepción G. Compuestos de oro en medicina-Crisoterapia. Anales de la Real Sociedad Española de Química. Segunda Edición. Universidad de Zaragoza. España- (2000)
[9] Laboratorios Argenol. Qué es plata coloidal. Available at: www.laboratorios-argenol.com
[10] M. Campos, J. Navarrete and J. Pérez. Efecto bactericida del fluoruro diamino de plata sobre microorganismos anaerobios facultativos y estrictos, aislados de conductos radiculares necróticos de dientes deciduos (in-vitro) Rev Sanid Milit; 62(5): 229-234. (2008)
[11] Univ. Nac. De Ingeniería, Lima. http://fc.uni.edu.pe/fc/
[12] W. Jefferson. El poder curativo de la plata coloidal. Un bactericida y antibiótico de amplio espectro totalmente. Primera Edición, (Editorial Ediciones Obelisco, 2005) p.80
[13] D. Denis and S. Andreyuk. 2019. Int. J. Nanotechnol., Vol. 16, Nos. 6/7/8/9/10
[14] Unidad de Desarrollo Tecnológico. 2010. Feria Internacional del plástico y del Caucho. Nanopartículas de Cobre.
[15] Información minera de Colombia. 2008. Nanopartículas de cobre serán usadas en cura del cáncer. Available at: www.imcportal.com
[16] E. Tejeda, L. Malpartida, E. Cubillo, C. Pecharromán, and J. Moya. 2009. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of a soda-lime glass containing copper nanoparticles Nanotechnology, 20 (50) DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/50/505701
[17] S. Wahyudi, S.Soepriyanto, Z. Mubarok, S. Sutarno. Synthesis and Applications of copper nanopowders.
IOP Series Materials Science Conference and Engineering 385(1)012014,2018. Doi : 10.1088/1757-899x/395/1/012014.
[18] J. Arroyo, A. Guzmán, S. Reátegui, C. Landauro, P. Ramírez and R. Pizarro. 2010. Bactericida a partir de nanopartículas de cobre. Available at: www.procobre.org. Accessed 26 June 2007
[19] G. Cárdenas and V. Lillo. 2007. Chemical reactions at nanometal particles. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. Vol. 50 (3): 603-612.
[20] R. Resnick, D. Halliday and K. Krane. Física. Vol. 2. 5ta ed. (1ra reimpresión. México, 2003).
[21] I. Sierra, D. Pérez, S. Gómez and S. Morante. Análisis instrumental: Algunas herramientas de enseñanza-aprendizaje adaptadas al Espacio Europeo de Educación Superior, 2º Edición. (Editorial Gesbiblo, 2010). Pp. 69, 207.
[22] A. Larraín. Criterios Eco toxicológicos para evaluar alteraciones ambientales y establecer parámetros de control: Importancia de los bioensayos de toxicidad. Revista Ciencia y Tecnología del Mar. Cona (Nº Especial, 1995). Pp. 39-47.
[23] JCediel, M. Cárdenas, A. García, L. Chuaire, C. Payán, V. Villegas and C. Sánchez. Manual de histología: tejidos fundamentales. (Editorial Universidad del Rosario, 2009). Pp. 36
[24] G. Hernández, A. Moreno, F. Zaragozá and A. Porras. Tratado de medicina farmacéutica. (Editorial medica Panamericana, 2010) pp. 136
[25] Helbing, W. Burkart. Tablas químicas para laboratorio de industria. (Editorial Reverté, 1985) p. 101
[26] Lenntech BV. Propiedades químicas de la plata. Available at: http://www.lenntech.es
Lenntech BV. Propiedades químicas de cobre. Efectos del cobre sobre la salud. Available at: http://www.lenntech.es
[27] J. Kotz. Modern Techniques in Chemistry: Infrared Spectroscopy. 2005, p. 100.
[28] S. Weininger and F. Stermitz. Organic Chemistry. (Editorial Reverté, 1988) p.306