ADSORPTION OF COOMASSIE BRILLIANT BLUE R-250 DYE ONTO NOVEL ACTIVATED CARBON PREPARED FROM NIGELLA SATIVA L. WASTE: EQUILIBRIUM, KINETICS AND THERMODYNAMICS RUNNING TITLE: ADSORPTION OF BRILLIANT BLUE DYE ONTO NIGELLA SATIVA L. WASTE ACTIVATED CARBON
- Adsorption,
- Coomassie brilliant blue dye,
- Chemical activation,
- Mechanism,
- Nigella sativa L. waste
Copyright (c) 2017 Nour T. Abdel-Ghani, Ghadir A. El-Chaghaby, El-Shaimaa A. Rawash, Eder C. Lima

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
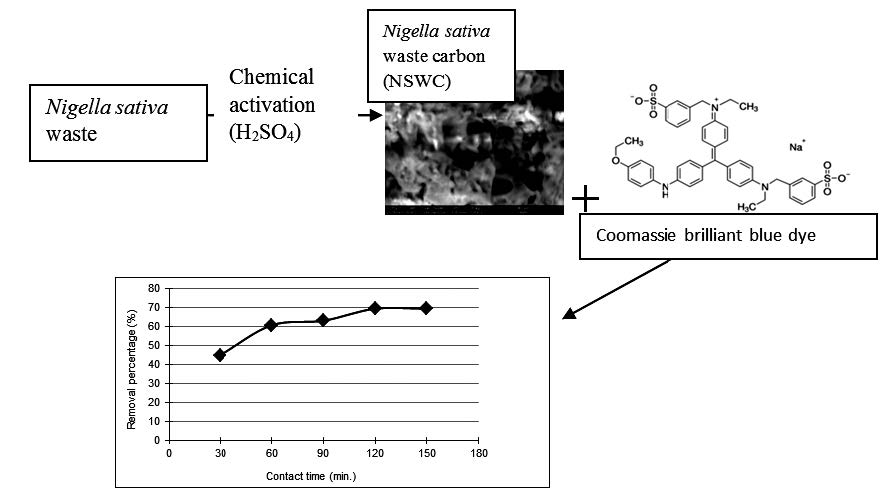
In this paper a novel adsorbent was prepared from Nigella sativa L. waste and used for the removal of Coomassie Brilliant Blue dye from wastewater. The preparation of Nigella sativa waste carbon (NSWC) was achieved by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to the precursor material at an impregnation ratio (1: 1) and the mixture was left overnight. The resulting material was washed with sodium bicarbonates and finally oven dried. The kinetics of coomassie brilliant blue adsorption onto NSWC was investigated by three kinetic models. The pseudo-second order model (R2 = 0.99) was the best model fitted the experimental data.
The equilibrium results revealed that Freundlich model was the best isotherm model fitted (R2= 0.994). Also the value of the Freundlich exponent (n) was found to be 1.174 suggesting the favorable dye adsorption onto NSWC. The thermodynamics results indicated negative values of ΔG proving the spontaneous nature of Brilliant Blue dye adsorption on NSWC. The exothermic nature of the adsorption was also confirmed by the negative value of change in enthalpy ΔH°. Also, the negative value of the activation entropy ΔS° demonstrates the decreased randomness at the solid–solution interface during adsorption. The present study results suggest the possible use of a waste such as Nigella sativa L. waste as a precursor for the development of a new cheap and efficient adsorbent that could be used in dyes removal from wastewater.
References
- Aji MM, Gutti B, Highina BK. APPLICATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON IN REMOVAL OF IRON AND MANGANESE FROM ALAU DAM WATER IN MAIDUGURI. Colomb J life Sci. 2015;17(1):35-39.
- Poinern GEJ, Senanayake G, Shah N, Thi-Le XN, Parkinson GM, Fawcett D. Adsorption of the aurocyanide, complex on granular activated carbons derived from macadamia nut shells – A preliminary study. Miner Eng. 2011;24(15):1694-1702. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2011.09.011.
- Gottipati R. Preparation and Characterization of Microporous Activated Carbon from Biomass and its Application in the Removal of Chromium ( VI ) from Aqueous Phase Department of Chemical Engineering. 2012;(January).
- Abdel-Ghani NT, El-Chaghaby G a., Zahran EM. Pentachlorophenol (PCP) adsorption from aqueous solution by activated carbons prepared from corn wastes. Int J Environ Sci Technol. 2015;12(1):211-222. doi:10.1007/s13762-013-0447-1.
- Patil BS, Kulkarni KS. Development of High Surface Area Activated Carbon From Waste Material. Int J Adv Eng Res Stud. 2012;I(II):109- 113.
- Karacan F, Ozden U, Karacan S. Optimization of manufacturing conditions for activated carbon from Turkish lignite by chemical activation using response surface methodology. Appl Therm Eng. 2007;27(7):1212-1218. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2006.02.046.
- Alqaragully MB. Removal of Textile Dyes ( Maxilon Blue , and Methyl Orange ) by Date Stones Activated Carbon. Int J Adv Res Chem Sci. 2014;1(1):48-59.
- Ahmad MA, Ahmad N, Bello OS. Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue Reactive Dye. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2014;(September 2014):37-41. doi: 10.1080/01932691.2014.925400.
- Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater. 2010;177(1- 3):70-80. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.047.
- Cimino G, Cappello RM, Caristi C, Toscano G. Characterization of carbons from olive cake by sorption of wastewater pollutants. Chemosphere. 2005;61:947-955. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.042.
- Olivares-Marín M, Fernández-González C, Macías-García a., Gómez- Serrano V. Preparation of activated carbon from cherry stones by physical activation in air. Influence of the chemical carbonisation with H2SO4. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2012;94:131-137. doi:10.1016/j.jaap.2011.11.019.
- Ahmad MA, Ahmad N, Bello OS. Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue Reactive Dye From Aqueous Solutions Using Watermelon Rinds as Adsorbent. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2014;(September 2014):37-41. doi:10.1080/01932691.2014.925400.
- Lagergren SY. Zur Theorie Der Sogenannten Adsorption Gelöster Stoffe.; 1898. Available at: http://books.google.com.eg/books/about/Zur_Theorie_der_sogenannten_Adsorption_g.html?id=LPUlHQAACAAJ&pgis=1. Accessed January 2, 2014.
- Ho YS, McKay G. A Comparison of Chemisorption Kinetic Models Applied to Pollutant Removal on Various Sorbents. Process Saf Environ Prot. 1998;76(4):332-340. Available at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957582098707657. Accessed January 2, 2014.
- Abdel Salam M, Burk RC. Thermodynamics and Kinetics Studies of Pentachlorophenol Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2009;210(1-4):101-111. doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0227-1.
- Ahmad MA, Rahman NK. Equilibrium , kinetics and thermodynamic of Remazol Brilliant Orange 3R dye adsorption on coffee husk-based activated carbon. Chem Eng J. 2011;170(1):154-161. doi:10.1016/j. cej.2011.03.045.
- Pelosi BT, Lima LKS, Vieira MGA. REMOVAL OF THE SYNTHETIC DYE REMAZOL BRILLIANT BLUE R FROM TEXTILE INDUSTRY WASTEWATERS BY BIOSORPTION ON THE MACROPHYTE Salvinia natans. Brazilian J Chem Eng. 2014;31(04):1035-1045.
- Kavitha D, Namasivayam C. Capacity of activated carbon in the removal of acid brilliant blue: Determination of equilibrium and kinetic model parameters. Chem Eng J. 2008;139(3):453-461. doi:10.1016/j. cej.2007.08.011.
- Sathishkumar P, Arulkumar M, Palvannan T. Utilization of agroindustrial waste Jatropha curcas pods as an activated carbon for the adsorption of reactive dye Remazol Brilliant Blue R ( RBBR ). J Clean Prod. 2012;22(1):67-75. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.09.017.
- Ratnamala GM, Shetty KV. Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue Dye from Dye-Contaminated Water by Adsorption Using Red Mud : Equilibrium , Kinetic , and Thermodynamic Studies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012;223(2012):6187-6199. doi:10.1007/s11270-012-1349-4.
- Ahmad MA, Herawan SG, Yusof AA. Equilibrium , Kinetics , and Thermodynamics of Remazol Brilliant Blue R Dye Adsorption onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Pinang Frond. ISRN Mech Eng. 2014;2014:1-7.
- Ata S, Imran Din M, Rasool A, Qasim I, Ul Mohsin I. Removal of Coomassie Brilliant Blue on Wheat Bran As a Low-Cost Adsorbent. J Anal Methods Chem. 2012;2012:405980. doi:10.1155/2012/405980.
- Demiral H. Adsorption of Textile Dye onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Industrial. Int Environ Appl Sci. 2008;3(5):381-389.
- Fierro V, Torné-Fernández V, Montané D, Celzard a. Adsorption of phenol onto activated carbons having different textural and Surface properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008;111(1-3):276-284. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.08.002.
- Ahmad a. a., Hameed BH, Aziz N. Adsorption of direct dye on palm ash: Kinetic and equilibrium modeling. J Hazard Mater. 2007;141(1):70-76. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.094.
- Hasan HA, Rozaimah S, Abdullah S, Tan N, Kamarudin SK. Isotherm equilibria of Mn 2 þ biosorption in drinking water treatment by locally isolated Bacillus species and sewage activated sludge. 2012;111:34-43. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.06.027.
- Mafra MR, Zuim DR, Ferreira MA. ADSORPTION OF REMAZOL BRILLIANT BLUE ON AN ORANGE PEEL ADSORBENT. Brazilian J Chem Eng. 2013;30(03):657-665.
- Dawood S, Sen TK. Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution by raw pine and acid-treated pine cone powder as adsorbent : Equilibrium , thermodynamic , kinetics , mechanism and process design. Water Res. 2012;46(6):1933-1946. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.009.
- Abbas M, Cherfi A, Kaddour S, Aksil T. Adsorption in simple batch experiments of Coomassie blue G-250 by apricot stone activated carbon — Kinetics and isotherms modelling. Desalin Water Treat. 2015;3994(October):1-12. doi:10.1080/19443994.2015.1067871.
- Zhong Z, Yang Q, Li X, Luo K, Liu Y, Zeng G. Preparation of peanut hull-based activated carbon by microwave-induced phosphoric acid activation and its application in Remazol Brilliant Blue R adsorption. Ind Crop Prod. 2012;37(1):178-185. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.12.015.
- Unal Gec gel and Hakan Kolanc|lar*. Adsorption of Remazol Brilliant Blue R on activated carbon prepared from a pine cone. Nat Prod Res Former Nat Prod Lett. 2011;(January 2014):37-41. doi:10.1080/14786419.2010.541878.
- Mahwish Asgher and Haq Nawaz. REMOVAL OF REACTIVE BLUE 19 AND REACTIVE BLUE 49 TEXTILE DYES BY CITRUS WASTE BIOMASS FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION: EQUILIBRIUM AND KINETIC STUDY. Can J Chem Eng. 2012;90(April):412-419. doi:10.1002/cjce.20531.
- Al-Anber ZA, Al-anber MAS, Al-anber ZA. Thermodynamics and Kinetic Studies of Iron ( III ) Adsorption by Olive Cak in a Batch System. J Mex Chem Soc. 2008;52(2):108-115.
- Munagapati VS, Yarramuthi V, Nadavala SK, Alla SR, Abburi K. Biosorption of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) by Acacia leucocephala bark powder: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Chem Eng J. 2010;157(2-3):357-365. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2009.11.015.
- Hern KA, Solache M. Removal of Brilliant Blue FCF from Aqueous Solutions Using an Unmodified and Iron-Modified Bentonite and the Thermodynamic Parameters of the Process. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013;224:1-11. doi:10.1007/s11270-013-1562-9.
- Ada K, Ergene A, Tan S, Yalc E. Adsorption of Remazol Brilliant Blue R using ZnO fine powder : Equilibrium , kinetic and thermodynamic modeling studies. J Hazard Mater. 2009;165(2009):637-644. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.036.