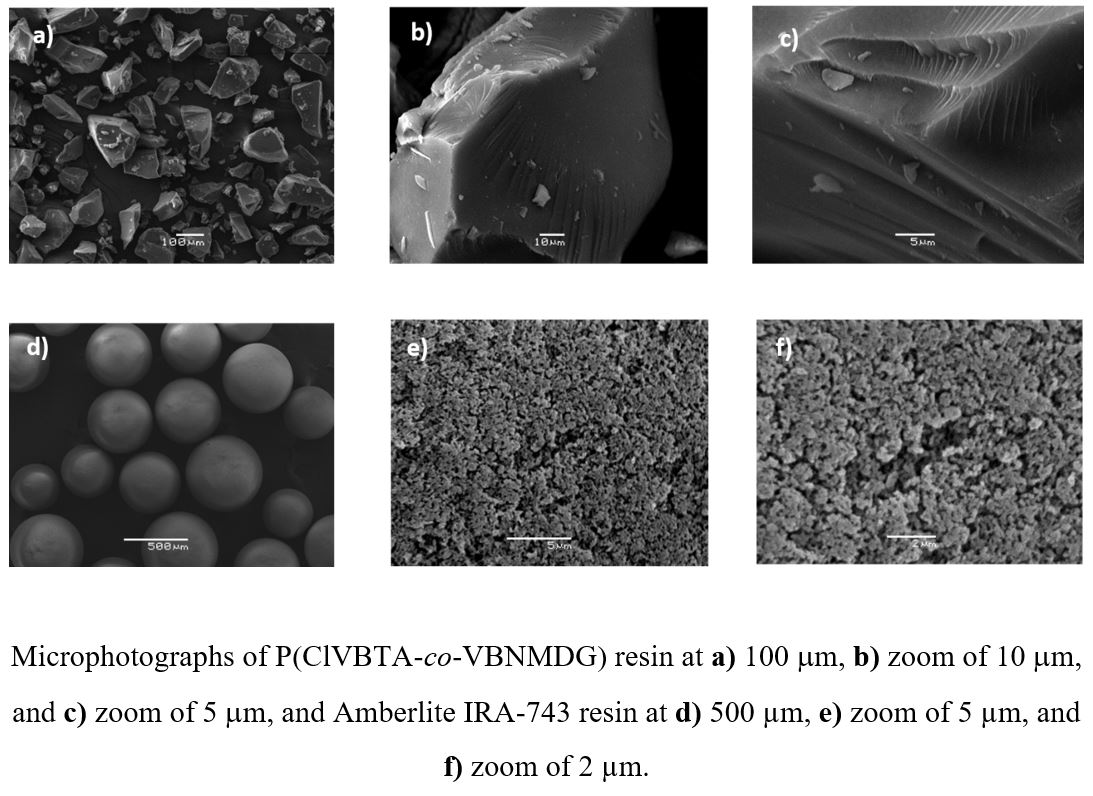
POLY(4-VINYLBENZYL) TRIMETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE-CO-(4-VINYLBENZYL)-N-METHYL-D-GLUCAMINE) COPOLYMER WITH REMOVAL PROPERTIES FOR VANADIUM (V) AND MOLYBDENIUM(VI). ADSORPTION ISOTHERM STUDY

- Resins,
- removal,
- metal ions,
- environment
Copyright (c) 2022 SChQ

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
It was studied the removal properties of poly(4-vinylbenzyl) trimethylammonium chloride–co-(4-vinylbenzyl)-N-methyl-D-glucamine) P(ClVBTA-co-VBNMDG) ion exchange resin towards vanadium (V) and molybdenum (VI), and compared with commercial resin Amberlite IRA-743 which contains the same functional group. The resin was characterized by FT-IR spectroscopy and SEM. Parameters like water adsorption capacity, effect of the pH, maximum retention capacity of the metal ions, elution, regeneration, selectivity, interferents effect, adsorption time, and adsorption isotherms were studied. All the studies were carried out by Batch equilibrium procedure. Thermodynamic parameters such as enthalpy, entropy, and free energy were calculated. The P(ClVBTA-co-VBNMDG) resin showed higher capacity to remove V(V) and Mo(VI) from water solution than that Amberlite IRA-743 commercial resin. The higher capacity displayed by P(VBNMDG) resin was attributed to the higher degree of swelling and the stronger active functional groups.
References
2 E. Nagy, desalination, 2009, 240, 2–6.
3 N. Sarwar, Saifullah, S. S. Malhi, M. H. Zia, A. Naeem, S. Bibia and G. Farida, J. Sci. Food Agric., 2010, 90, 925–937.
4 N. Sarwar, W. Ishaq, G. Farid, M. Rashid, M. Imran, M. Geng and S. Hussain, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2015, 122, 528–536.
5 D. E. Rusyniak, A. Arroyo, J. Acciani, B. Froberg, L. Kao and B. Furbee, 1 D. E. Rusyniak, A. Arroyo, J. Acciani, B. Froberg, L. Kao and B. Furbee, Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxicl, 2010, 2, 365–396.
6 B. Barkhordar and M. Ghiasseddin, Iran. J. Heal. Sci. Eng., 2004, 1, 58–64.
7 F. Fu and Q. Wang, J. Environ. Manage., 2011, 92, 407–418.
8 J. Li, Z. Zhao, C. Cao, G. Zhang and G. Huo, RMHM, 2012, 30, 180–184.
9 Z. Zhao, C. Cao, X. Chen and G. Huo, Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108, 229–232.
10 K. Park, H. Kim and P. K. Parhi, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2010, 74, 294–299.
11 L. Zeng and C. Yong, Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 101, 141–147.
12 E. K. Alamdari, D. Darvishi, D. F. Haghshenas, N. Yousefi and S. K. Sadrnezhaad, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2012, 86, 143–148.
13 D. M. Imam, Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 180, 172–179.
14 Z. Zhu, K. Tulpatowicz, Y. Pranolo and C. Yong, Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 154, 72–77.
15 F. Pagnanelli, F. Ferella, I. De Michelis and F. Vegliò, Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 110, 67–72.
16 K. Ho, D. Mohapatra and B. R. Reddy, J. Hazard. Mater.,2006, 138, 311–316.
17 S. Y. Seo, W. S. Choi, T. J. Yang, M. J. Kim and T. Tran, Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 129–130, 145–150.
18 A. A. Basualto, Carlos, Jose Marchese, Fernando Valenzuela, Talanta, 2003, 59, 999–1007.
19 F. Valenzuela, C. Basualto and A. Acosta, 2004, 72, 309–317.
20 Y. Fu, Q. Xiao, Y. Gao, P. Ning, H. Xu and Y. Zhang, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2018, 28, 1660–1669.
21 P. Orrego, J. Hernández and A. Reyes, Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 184, 116–122.
22 B. Padh, P. C. Rout, G. K. Mishra, K. R. Suresh and B. R. Reddy, Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 184, 88–94.
23 T. H. Nguyen and M. S. Lee, Hydrometallurgy, 2013 ,136, 65-70.
24 Z. Zhuo, L. I. Xiaobin and Z. Qingjie, RARE Met., 2010, 29, 115–120.
25 B. L. Rivas, H. A. Maturana and E. Pereira, Die Angew. Makromol. Chemie, 1994, 220, 61–74.
26 D. C. Crans, J. J. Smee, E. Gaidamauskas and L. Yang, Chem. Rev. 104, 849–902
27 B. Zhang, C. Tian, Y. Liu, L. Hao, Y. Liu, C. Feng, Y. Liu and Z. Wang, Bioresour. Technol., 2015, 179, 91–97.
28 R. R. Moskalyk and A. M. Alfantazi, Miner. Eng., 2003, 16, 793–805.
29 H. Peng, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 103-313.
30 J. J. Cruywagen, Adv. Inorg. Chem, 2000, 49, 127-182
31 M. Imtiaz, M. Shahid, S. Xiong, H. Li, M. Ashraf, S. Muhammad, M. Shahzad, M. Rizwan and S. Tu, Environ. Int., 2015, 80, 79–88.
32 A. S. Tracey, G. R. Willsky and E. S. Takeuchi, Vanadium: Chemistry, Biochemistry, Pharmacological, and Practical Applications, CRC Press, 1 st ed., 2007.pp 1-2
33 J. Rinklebe, V. Antoniadis, S. M. Shaheen, O. Rosche and M. Altermann, Environ. Int., 2019, 126, 76–88.
34 Urbano, B. F. Resinas Nanocompósitos y Su Potencial Aplicación En Procesos de Intercambio Iónico, Universidad de Concepción, 2012.
35 Misak, N. Z. Adsorption Isotherms in Ion Exchange Reactions. Further Treatments and Remarks on the Application of the Langmuir Isotherm. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 97 (2), 129–140.
36 Alexandratos, S. D. New Polymer-Supported Ion-Complexing Agents: Design, Preparation and Metal Ion Affinities of Immobilized Ligands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139 (3), 467–470.
37 Dambies, L.; Salinaro, R.; Alexandratos, S. D. Immobilized N-Methyl-D-Glucamine as an Arsenate-Selective Resin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38 (22), 6139–6146.