- Asenapine,
- HPLC,
- Ion-pair chromatography,
- Tablet analysis
Copyright (c) 2017 Sakine Atila Karaca, Duygu Yeniceli Uğur

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
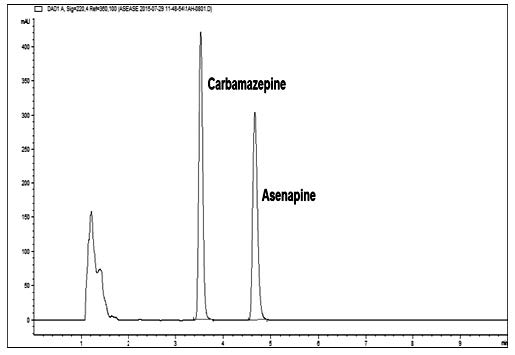
In this study, a new, simple and specific stability indicating ion-pair LC method was developed and fully validated for the determination of asenapine in tablets. The analysis was performed on an Agilent Eclipse XDB-C8 column (4.6 x 150 mm, 3.5 μm particles) at 30˚C. A mixture of phosphate buffer (pH 3, 20 mM) containing 10 mM 1-heptane sulfonic acid and acetonitrile, (60:40, v/v) at a flow rate of 1 mL min-1 was used as mobile phase. Detection was performed by a diode array detector at 220 nm. The developed method was validated according to related ICH guideline and US Pharmacopeia and it was suitable in terms of accuracy, precision, specificity, robustness and stability. The method was linear in the concentration range of 0.5-100 μg mL-1. Limit of detection and limit of quantification values were calculated as 0.0836 μg mL-1 and 0.2788 μg mL-1, respectively. This ion-pair LC method was applied successfully for the determination of asenapine in its sublingual tablets.
References
- R. Vardanyan, V. Hruby, Antipsychotics (Neuroleptics). Synthesis of essential drugs, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006.
- D. Bishara, D. Taylor, Drugs. 68, 2269, (2008).
- B. A. Ellenbroek, Neuropharmacology. 62, 1371, (2012).
- L. Citrome, Expert Opin Drug Saf. 13, 803, (2014).
- Saphris (asenapine) sublingual tablets, FDA drug approval package. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2009/022117s000_ ChemR.pdf (accessed Feb 11, 2016).
- J. M. Gonzalez, P. M. Thompson, T. A. Moore, Patient Prefer Adher. 5, 333, (2011).
- L. Citrome, Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 10, 893, (2014).
- L. Kovatsi, A. Titopoulou, A. Tsakalof, V. Samanidou, J Liq Chrom Relat Tech. 38, 1666, (2015).
- T. de Boer, E. Meulman, H. Meijering, J. Wieling, P. Dogterom, H. Lass, Biomed Chromatogr. 26, 156, (2012).
- T. de Boer, E. Meulman, H. Meijering, J. Wieling, P. Dogterom, H. Lass, Biomed Chromatogr. 26, 1461, (2012).
- N. Ansermot, M. Brawand-Amey, A. Kottelat, C. B. Eap, J Chromatogr A. 1292, 160, (2013).
- A. V. B. Reddy, N. Venugopal, G. Madhavi, J Pharm Anal. 3, 394, (2013).
- L. Patteet, K. E. Maudens, B. Sabbe, M. Morrens, M. De Doncker, H. Neels, Clin Chim Acta. 429, 51, (2014).
- C. Sempio, L. Morini, C. Vignali, A. Groppi, J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 970, 1, (2014).
- C. Miller, O. Pleitez, D. Anderson, D. Mertens-Maxham, N. Wade, J Anal Toxicol. 37, 559, (2013).
- K. Aarelly, M. K. Thimmaraju, N. Raghunandan, J App Pharm Sci. 2, 141, (2012).
- O. A. Halima, T. P. Aneesh, R. Ghosh, N. R. Thomas, Der pharma chem. 4, 644, (2012).
- T. R. Parthasarathi, T. S. Srinivas, M. V. Sri, S. S. Ram, M. M. Basha, P. Rajesh, Int J Pharm Bio Sci. 3, 360, (2012).
- U. K. Chhalotiya, K. K. Bhatt, D. A. Shah, J. R. Patel, Sci. Pharm. 80, 407, (2012).
- R. B. Patel, N. S Naregalkar, M. R. Patel, J Liq Chrom Relat Tech., 38, 1731, (2015).
- ICH, Harmonized Tripartite Guideline, Q2 (R1): Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology, (2005).
- The United States Pharmacopeia 29, Easton, (2006).
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Reviewer guidance, Validation of chromatographic methods, FDA, Rockville, MD, (1994).
- G. A. Shabir, J Chromatogr A. 987, 57, (2003).
- S. Atila Karaca, MSc Thesis, Determination and Validation of Asenapine in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms by a Stability Indicating HPLC Method, Anadolu University, (2016).