THE THEORETICAL CALCULATIONS AND EXPERIMENTAL MEASUREMENTS OF ACID DISSOCIATION CONSTANT AND THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF GLYCYL-ASPARTIC ACID IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION AT DIFFERENT TEMPERATURES

- Glycyl aspartic acid,
- acid dissociation constant,
- thermodynamic properties,
- density function theory,
- Ab initio.
Copyright (c) 2020 Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
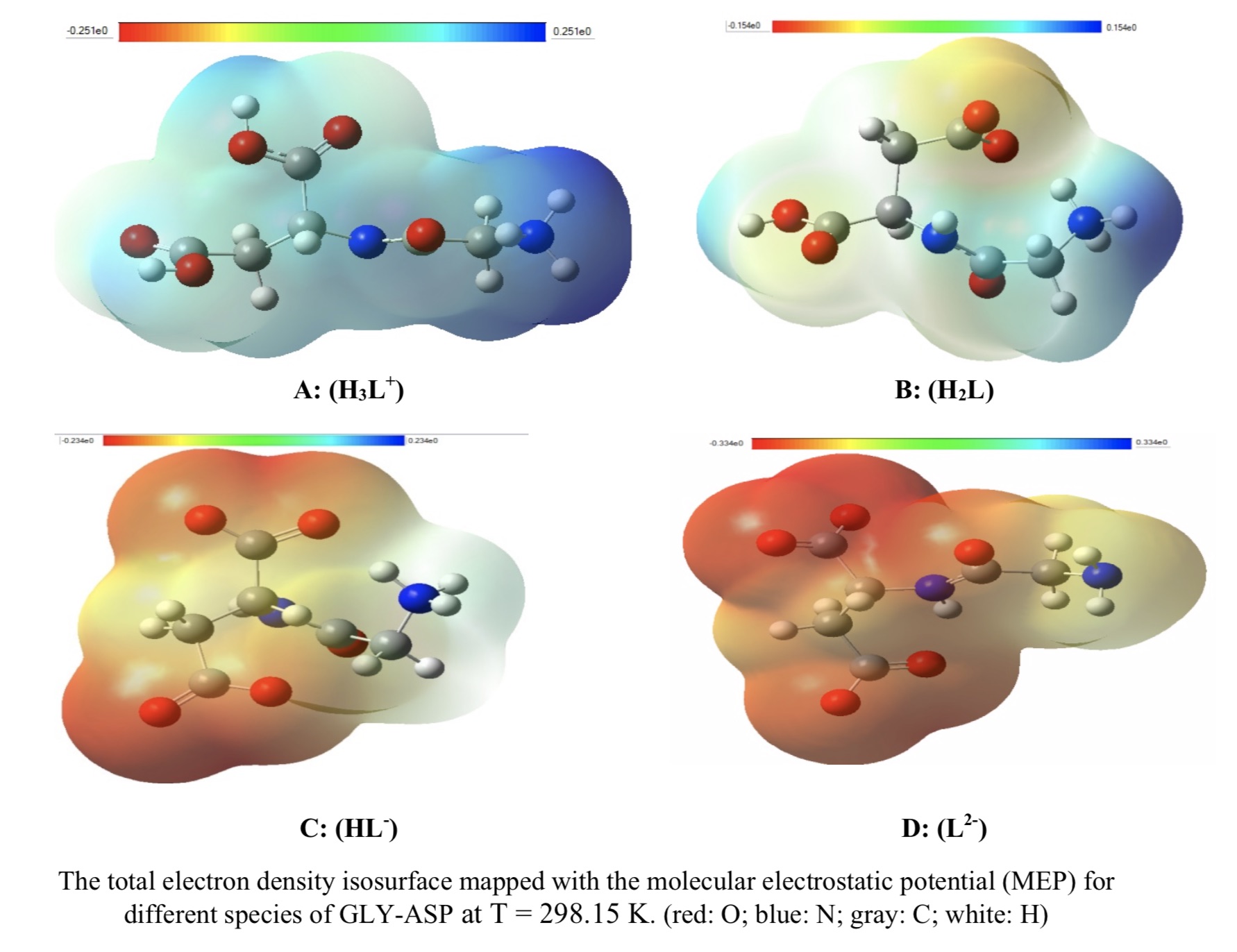
In this research work, a potentiometric technic was used to measure the acidic dissociate constants (pKa,s) for glycyl aspartic acid (GLY-ASP) at temperatures (298.15, 303.15, 313.15, and 318.15) K and in 0.1 mol/l ionic strength of chloride sodium. Using this data, we calculated the thermodynamic properties (changes of enthalpy, ΔH, changes of entropy, ΔS, and changes of Gibbs free energy, ΔG) for acidic dissociation reaction of GLY-ASP. All analyses of data were studied in pH = 1.5-11 and in the aqueous solution. In addition, the value of the acid dissociation constants (pKa1, pKa2, and pKa3), the optimized structure, and the thermodynamic properties of GLY-ASP were calculated in aqueous solution at various temperatures by ab initio and DFT methods. Density function theory (DFT) has been used based on the B3LYP/6-31+G(d) theory to explain the obtained acid dissociation constants of GLY-ASP as well as interactions between solvent and solvated cation, anion, and neutral species of GLY-ASP. Thomasi’s method was used to analyze the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the water molecule and various species of GLY-ASP. In addition, the energy gap of anionic, cationic, and neutral species of GLY-ASP were obtained for dissociation reactions of GLY-ASP. Finally, for GLY-ASP, the theoretically calculated and experimentally determined pKa,s were compared together and a good agreement was observed between them in the first, second, and third ionization constant of GLY-ASP.
References
- M.D. Beachy, D, Chasman, R.B. Murphy, T.A. Halgren, R.A. Friesner, Accurate ab initio quantum chemical determination of the relative energetics of peptide conformations and asseessment of empirical force fields., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119 (1997) 5908-5920.
- M. Kanost, J.K. Kawooya, J.H. Law, R.O. Ryan, M.C. Van Heusden, R. Ziegler, Insect hemolymph proteins, Advances in Insect Physiology. 22 (1990) 299-396
- P.D. Bailey, an Introduction to peptide chemistry, John Wiley and Sons. 1992, New York.
- A. Catsch, A.E. Harmuth-Hoene, Pharmacology and therapeutic applications of agents used in heavy metal poisoning. Pharmacol. Ther. 1 (1976) 1-118.
- M. Monajjemi, F. Gharib, H. Aghaei, G. Shafiee, A. Thghvamanesh, A. Shamel, Thallium (I) complexes of some sulfur containing ligands. Main Group Met. Chem. 26 (2003) 39-47.
- Ju. Lurie, Handbook of Analytical Chemistry, 1st ed.; Mir: Moscow, 1975.
- Thomas, G. Medicinal Chemistry: An Introduction; John Wiley and Sons: West Sussex 2000.
- W. Stumm, J.J. Morgan, Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters; Wiley-Interscience. 1996, New York.
- H. Wan, J. Ulander, High–throughput pKa screening and prediction amenable for ADME profiling. Expert. Drug. Metab. Toxicol. 2 (2006) 139-155.
- A. Albert, The determination of ionization constants. a laboratory manual. Springer, New York City, 2012.
- S. Sharifi, D. Nori-shargh, A. Bahadory, Complexes of Thallium (I) and Cadmium (II) with Dipeptides of L-phenylalanylglycine and Glycyl-L-phenylalanine. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 18 (2007) 1011-1016.
- P. Janos, Determination of equilibrium constants from chromatographic and electrophoretic measurements. J. Chromatogr. A. 1037 (2004) 15-28.
- A. Avdeef, J.E. Comer, S.J. Thomson, pH-Metric log P. 3. Glass electrode calibration in methanol-water, applied to pKa determination of water-insoluble substances. Anal. Chem. 65 (1993) 42-49.
- K.Y. Tam, K. Takacs-Novak, Multi-wavelength spectrophotometric determination of acid dissociation constants: a validation study. Anal. Chim. Acta. 434 (2001) 157-167.
- J. Wang, Analytical electrochemistry (3rd ed) John Wiley & Sons. New York: John Wiley & Sons. 2006.
- K. Mohle, H.J. Hofmann, Stability order of basic peptide conformations reflected by density functional theory. J. Mol. Model. 4 (1998) 53-60.
- S.J. Archer, P.J. Domaille, E.D. Laue, New NMR methods for structural studies of proteins to aid in drug design. Ann. Rep. Med. Chem. 31 (1996) 299-307.
- B.J. Smith, L. Radom, Evaluation of accurate gas-phase acidities. J. Phys. Chem. 95 (1991) 10549-10551.
- D.D. Perrin, B. Dempsey, E.P. Serjeant, pKa Prediction for organic acids and bases. London: Chapman & Hall. pp. 21-26, 1981.
- R. Gomes-Bombarelli, M. Gonzalez-Perez, M.T. Perez-Prior, E. Calle, J. Casado, Computational Study of Eseters and Lactones. A Case Study of Diketenese. J. Org. Chem. 74 (2009) 4943-4948.
- M. Alimohammady, M. Jahangiri, F. Kiani, H. Tahermansouri, Molecular modeling, pKa and thermodynamic values of asthma drugs. Med. Chem. Res. 27 (2017) 95-114.
- C. Lee, W. Yang, R.G. Parr, Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B. 37 (1988) 785-789.
- A.D. Becke, Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 98 (1993) 5648-5652.
- M.J. Frisch, G.W. Trucks, H.B. Schlegel, G.E. Scuseria, Gaussian 98, Revision A.6, Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, 1998.
- S. Miertus, E.J. Tomasi, Approximate evaluations of the electrostaticfree energy and internal energy changes in solution processes. Chem. Phys. 65 (1982) 239-245.
- S. Miertus, E. Scrocco, J. Tomasi, Electrostatic interaction of a solute with a continuum. A direct utilizaion of AB initio molecular potentials for the prevision of solvent effects. Chem. Phys. 55 (1981) 117-129.
- R. Cammi, J. Tomasi, Remarks on the use of the apparent surface charges (ASC) methods in solvation problems: Iterative versus matrix‐inversion procedures and the renormalization of the apparent charges. J. Comput. Chem. 16 (1995) 1449-1458.
- M.T. Beck, I. Nagypal, Chemistry of Complex Equilibria. Ellis Harwood, 1990, New York.
- E. Kilic, N. Aslan, Determination of autoprotolysis constants of water-organic solvent mixtures by potentiometry. Microchim. Acta. 151 (2005) 89-92.
- A. Farajtabar, F. Naderi, F. Gharib, Autoprotolysis in water/methanol/NaCl ternary systems. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 78 (2013) 1561-1567.
- N. Maleki, B. Haghighi, A. Safavi, Evaluation of formation constants, molar absorptivities of metal complexes, and protonation constants of acids by nonlinear curve fitting using microsoft excel solver and user-defined function. Microchem. J. 62 (1999) 229-236.
- J.A. Dean, Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 15th Ed.; McGraw-Hill. 1999, New York.
- H.A. Laitinen, W.E. Harris, Chemical Analysis; McGraw-Hill. 1975, New York.
- P.W. Atkins, Physical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Oxford University Press. 1998, England.
- Jeffrey, G.A. an Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding, Oxford University Press. 1997, Oxford.
- Y. Marcus, The properties of organic liquids that are relevant to their use as solvating solvents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 22 (1993) 409-416.
- F. Kiani, S.B. Hosseini, S.A. Shahidi, F. Koohyar, Ab initio and DFT studies on ionization of saccharin in aqueous solution. Chemistry Today 34 (2016) 26-29.
- A. Nag, B. Dey, Computer-aided drug design and delivery systems, 1976.
- J.B. Chaires, Calorimetry and thermodynamics in drug design. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 37 (2008) 135-151.
- A.J. Ruben, Y. Kiso, E. Freire, Overcoming roadblocks in lead optimization: a thermodynamic perspective. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 67 (2006) 2-4.
- B.K. Shukla, U. Yadava, M. Roychoudhury, Theoretical explorations on the molecular structure and IR frequencies of 3- phenyl-1-tosyl-1H-pyrazolo [3, 4-d] pyrimidin-4-amine in view of experimental results. J. Mol. Liq. 212 (2015) 325-330.
- M. Ogurlu, Adsorption of a textile dye onto activated sepiolite, J. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials. 119 (2009) 276-283.
- Y.D. Arzu, A comparative study on determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of biosorption of copper (II) and lead (II) ions onto pretreated Aspergillusniger, J. Biochem. Eng. 28 (2006) 187-195.
- P.M. Pimentel, M.A.F. Melo, D.M.A. Melo, A.L.C. Assuncao, D.M. Henrique, J.r C.N, Siva, G. Gonzalez, Kinetics and thermodynamics of Cu (II) adsorption on oil shale wastes, J. Fuel Processing Technology. 89 (2008) 62-67.
- J.A. Mondragon‐Sanchez, R. Santamaria, R. Garduno‐Juarez, Docking on the DNA G‐quadruplex: A molecular electrostaticpotential study. Biopolymers. 95 (2011) 641-650.
- P. Politzer, D.G. Truhlar, Chemical Applications of Atomic andMolecular Electrostatic Potentials: Reactivity, Structure, Scattering,and Energetics of Organic, Inorganic, and Biological Systems.Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013.
- R.H. Petrucci, W.S. Harwood, F.G. Herring, J.D. Madura, General Chemistry: Principles & Modern Applications. 9th Ed. New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc, 2007.
- T. Nogrady, D.F. Weaver, Medicinal Chemistry: A Molecular andBiochemical Approach. Oxford University Press, USA, 2005.
- A. Asghar, A. Aziz Abdul Raman, W.M.A. Wan Daud, A. Ramalingam, Reactivity, stability, and thermodynamic feasibility of H2O2/H2O at graphite cathode: application of quantum chemical calculations in MFCs. American Institute of Chemical Engineers, DOI 10.1002/ep.12806, 2017.